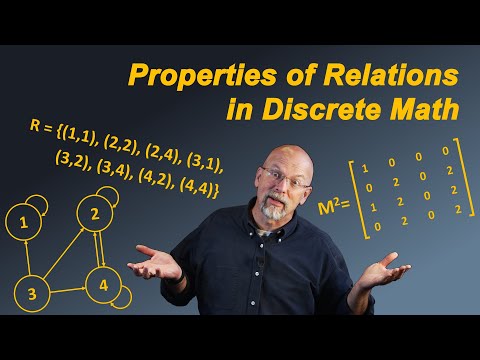
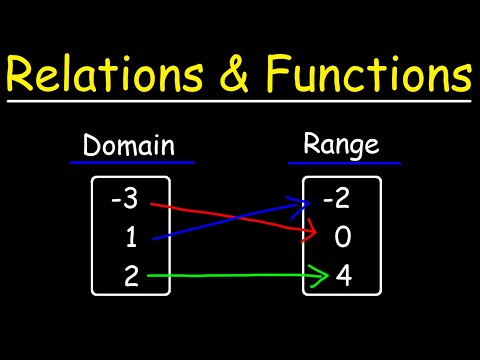
Relations Class 12 For Live Classes, Concept Videos, Quizzes, Mock Tests & Revision Notes please see our Website/App: Our Website: Android App: CBSE Class 12 Courses: CBSE Class 11 Courses: CBSE Class 10 Courses: CBSE Class 9 Courses: CBSE Class 8 Courses: ICSE Class 10 Courses: ICSE Class 9 Courses: ICSE Class 8 Courses: IGCSE Courses: Artificial Intelligence: Python Coding: Java Coding: Facebook page: In mathematics, a relation is a way of showing a connection or relationship between elements of two sets. It tells us how elements from one set are related to elements from another or the same set. If we have two sets, say A and B, a relation R from A to B is a subset of the Cartesian product A × B. That means R is a set of ordered pairs (a, b) where a is from set A and b is from set B. If A and B are the same set, it is called a relation on a set. Types of Relations: 1. Reflexive relation: A relation R on a set A is reflexive if for every element a in A, the pair (a, a) is in R. Example: "is equal to" — Every element is equal to itself. 2. Symmetric relation: A relation R is symmetric if whenever (a, b) is in R, then (b, a) is also in R. Example: "is a sibling of" — If A is a sibling of B, then B is a sibling of A. 3. Transitive relation: A relation R is transitive if whenever (a, b) and (b, c) are in R, then (a, c) is also in R. Example: "is an ancestor of" — If A is an ancestor of B, and B is an ancestor of C, then A is an ancestor of C. Equivalence relation: A relation that is reflexive, symmetric, and transitive. At Manocha Academy, learning Science and Math is Easy! The school coursework is explained with simple examples that you experience every day! Yes, Science & Math is all around you! Let's learn every day from everyday life!
- 7536Просмотров
- 8 месяцев назадОпубликованоManocha Academy
Relations and Functions Class 12
Похожее видео
Популярное
маленький шеф карусель
jarmies
Robinhood sreeleela songs
Bing si fa male
ВОЛШЕБНАЯ КАРУСЕЛЬ
сваты все серии
ПОРЧЕННЫЙ
Писик Лупидиду мультфильм
фіксики
Красная гадюка 5-8 серия
dora
Семья от а до Я
плюсплюс
мультик
Красная гадюка 11 серия
hentai
girls feet
Трое из Простоквашино
Переходный
Beast rogue lion
poland warsaw metro ride from dworzec wilenski
Умизуми
Universal 1998 effects
poterianij snaiper 2 seria
Зворотний напрямок
jarmies
Robinhood sreeleela songs
Bing si fa male
ВОЛШЕБНАЯ КАРУСЕЛЬ
сваты все серии
ПОРЧЕННЫЙ
Писик Лупидиду мультфильм
фіксики
Красная гадюка 5-8 серия
dora
Семья от а до Я
плюсплюс
мультик
Красная гадюка 11 серия
hentai
girls feet
Трое из Простоквашино
Переходный
Beast rogue lion
poland warsaw metro ride from dworzec wilenski
Умизуми
Universal 1998 effects
poterianij snaiper 2 seria
Зворотний напрямок
Новини