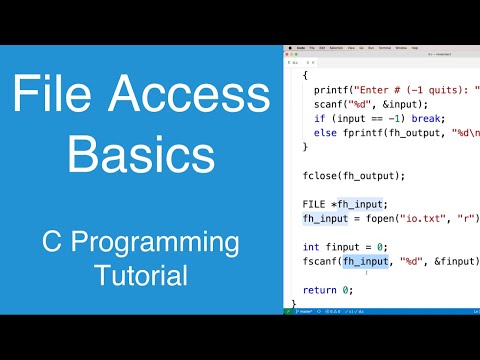
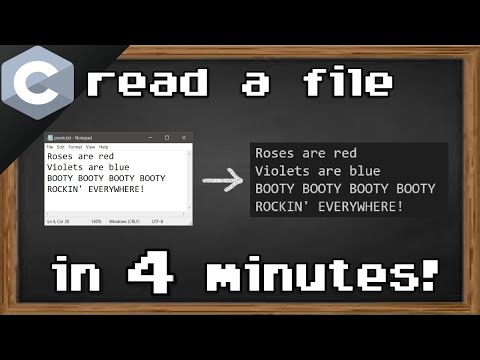
In this video, you will learn the fundamentals of file handling in C programming. File handling is a crucial aspect of many programming projects, and in this tutorial, you will explore everything from why you need to use files to how to create, open, and work with them in C. Throughout the video, you will understand the significance of files in programming, specifically in C, where variables are used to store data temporarily while the program is running. However, when the program ends, that data disappears. To persist data beyond the program’s execution, files are used. You will learn about two main types of files in C: text files and binary files. While text files store data in readable characters, binary files store data in binary format, which can’t be read easily by humans. The video will then guide you through various file operations, such as creating and opening files. You will discover how to use the `fopen()` function to open files in different modes like reading, writing, and appending, and how to manage files with the `FILE` structure defined in `stdio.h`. You will learn in detail about the different file opening modes, such as `r`, `w`, `a`, `r+`, `w+`, and `a+`, and how each one behaves differently depending on the existence of the file. The video also covers the binary file equivalents for these modes by adding the `b` keyword (e.g., `rb`, `wb`, `ab`) for handling binary files. By the end of this video, you will know how to manage file pointers, check if files open successfully, and close files when you're done working with them using the `fclose()` function. Practical examples will be shown, such as how to create a file if it doesn’t exist or overwrite its contents, as well as how to append new data to an existing file. If you're new to file handling in C, this video will give you a solid understanding of how to create and manipulate files in your own programs. If you're looking to practice, you are encouraged to experiment with the code in the video, modify the file opening modes, delete and create new files, and observe how each mode works in different scenarios. In future videos, you will learn how to write to and read from files, so stay tuned! Our Website Social Media Facebook Twitter Instagram
- 13029Просмотров
- 8 месяцев назадОпубликованоLearningLad
What are Files & How to Create and Open them : File Handling Introduction in C Language
Похожее видео
Популярное
Кормление
Городскои снаипер 8
Красная гадюка 8 серия
moden toking
чаггингтон
ПОТЕРЯННЫЙ СНАЙПЕР 5 сери
klaskyklaskyklaskyklasky joey 2 do go
Потерянный снайпер 3 серия
Robinhood sreeleela
Resila osta
бурное безрасудство 1
макс и катя тележка
Nickelodeon
ну погоди 18 выпуск
Tel ali
Тваринки-Бляшанки
Not scary universal g major 4
Щенячий патруль
poterianij snaiper 4 seria
CPXV02 14
комедия
Красный тарантул 3 серия
хасбро раша операция
Я - жена вашого мужа 2
Halloween boo boo song
Городскои снаипер 8
Красная гадюка 8 серия
moden toking
чаггингтон
ПОТЕРЯННЫЙ СНАЙПЕР 5 сери
klaskyklaskyklaskyklasky joey 2 do go
Потерянный снайпер 3 серия
Robinhood sreeleela
Resila osta
бурное безрасудство 1
макс и катя тележка
Nickelodeon
ну погоди 18 выпуск
Tel ali
Тваринки-Бляшанки
Not scary universal g major 4
Щенячий патруль
poterianij snaiper 4 seria
CPXV02 14
комедия
Красный тарантул 3 серия
хасбро раша операция
Я - жена вашого мужа 2
Halloween boo boo song
Новини