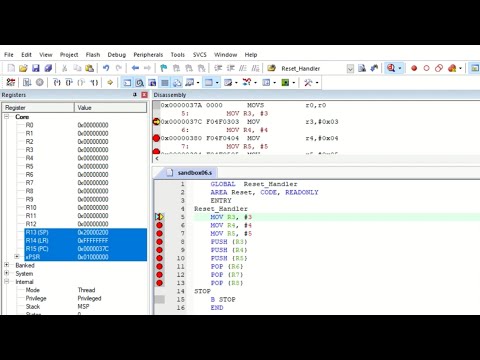
Emulator link: How to read/write Hex: How stack allocations work: (Code below chapters!) 00:00 Recursion in Assembly 00:56 How the stack works 04:38 Start of recursion call 09:08 The collapse of the stack (end of recursion) 14:20 How long until a stack overflow occurs? 15:38 What would cause a stack overflow here? 16:00 How to output to console in Assembly 21:05 Using an emulator to run Assembly code *** CODE BELOW *** I will set up a repository soon! ================= format ELF64 executable 3 segment readable executable entry _main mov rbp, rsp _main: mov rbp, rsp mov rdi, 3 call _countdown xor rdi, rdi call _exit _countdown: push rbp mov rbp, rsp push rdi mov rax, rdi add rax, 48 sub rsp, 8 mov rdi, 1 mov [rbp-16], eax lea rsi, [rbp-16] mov rdx, 1 mov rax, 1 syscall add rsp, 8 pop rdi cmp rdi, 0 je _end__recursion dec rdi call _countdown _end__recursion: pop rbp ret _exit: mov rax, 60 syscall ================= *** C code below *** int main() { countdown(3); return 0; } void countdown (int arg) { char digit = (arg + '0'); write(1, &digit, 1); // printf("%c", digit); if(arg == 0) return; arg = arg - 1; countdown(arg); return; // I hope the teacher allows me to change the 'F'! }
- 1929Просмотров
- 8 месяцев назадОпубликованоMxy
How Recursion Works in Assembly | Machine Code | Programming Fundamentals
Похожее видео
Популярное
Холодное сердце сео
СТРАЖИ ПРАВОСУДИЯ 4
Universal 1997 2012 g. Major 4
Волчий берег11серии
энчантималс реклама
малыш вилли 03
Потеряний снайпер2
томас и его друзья песня
Красная гадюка 16 серия
красный тарантул
Лихач 2025
реклама для детей
Актеры красной гадюки
барбарики барбарелла
Чудо
СТРАЖИ ПРАВОСУДИЯ 5
потерянный снайпер 11»
союзмультфильм игрушки
Финал
Городской снайпер 3
СУПЕР КРЫЛЬЯ
moden toking
Грань правосудия 4
СТРАЖИ ПРАВОСУДИЯ 4
Universal 1997 2012 g. Major 4
Волчий берег11серии
энчантималс реклама
малыш вилли 03
Потеряний снайпер2
томас и его друзья песня
Красная гадюка 16 серия
красный тарантул
Лихач 2025
реклама для детей
Актеры красной гадюки
барбарики барбарелла
Чудо
СТРАЖИ ПРАВОСУДИЯ 5
потерянный снайпер 11»
союзмультфильм игрушки
Финал
Городской снайпер 3
СУПЕР КРЫЛЬЯ
moden toking
Грань правосудия 4
Новини