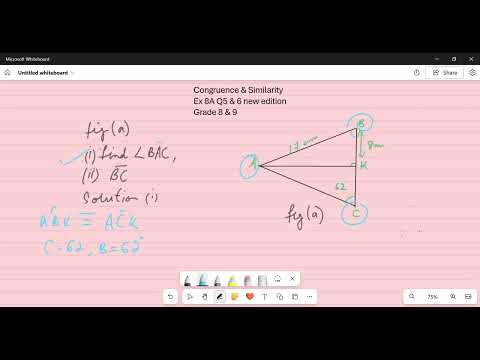
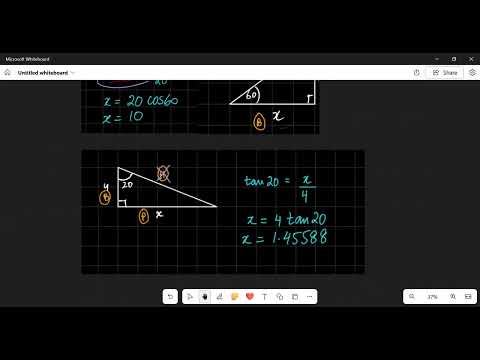
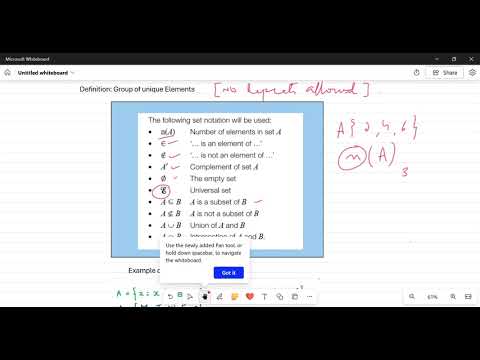
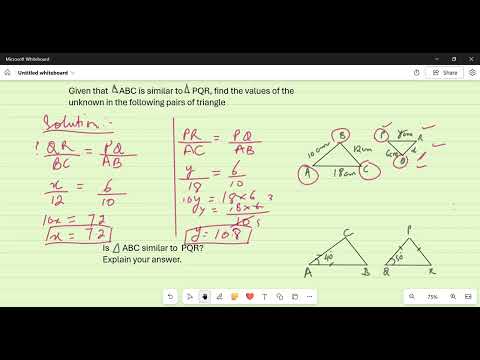
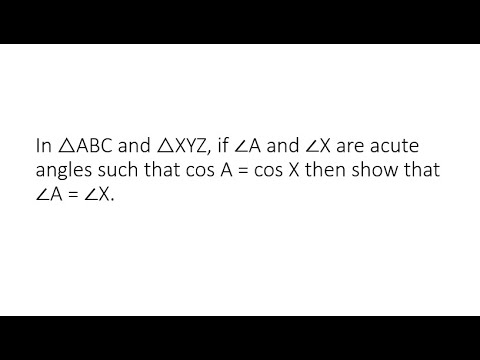🔺 What is the Pythagorean Theorem? The Pythagorean Theorem is a fundamental principle in geometry that applies to right-angled triangles. It states: In a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides (the two legs). Why Is It Important? — Key Uses & Applications This theorem is widely used because: It connects algebra with geometry in a simple but powerful way. It helps you calculate unknown side lengths in right triangles — for example, if you know two sides, you can find the third. It’s the basis of many real-world applications: construction, navigation, architecture, physics, engineering, image processing, and even game development. It underpins more advanced mathematical ideas, such as distance formula in coordinate geometry, 3D distance calculations, and verifying whether a triangle is right-angled.
- 37Просмотров
- 1 неделя назадОпубликованоMath Made Simple
THE PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM #mathtutorial # GCSE
Похожее видео
Популярное
союзмультфильм игрушки
Bing shut down itv
Rosie Misbehaves on a road trip grounded
обнаженная
Баскервиллей
ПОТЕРЯННЫЙ СНАЙПЕР2
ПОТЕРЯННЫЙ СНАЙПЕР 3
Чудо
бонифация
алиса в стране чудеса
барбоскины тайный
Go Diego go
Universal 1997 effects not scary
Красная годюка 5 часть
Universal 2013 effects
Фивел
Universal major 4
смешарики
cum
Pushpa 2 rashmika mandanna
Поиск - потеряний снайпер
masculine men
Fap teen
Finger family boo boo song
Bing shut down itv
Rosie Misbehaves on a road trip grounded
обнаженная
Баскервиллей
ПОТЕРЯННЫЙ СНАЙПЕР2
ПОТЕРЯННЫЙ СНАЙПЕР 3
Чудо
бонифация
алиса в стране чудеса
барбоскины тайный
Go Diego go
Universal 1997 effects not scary
Красная годюка 5 часть
Universal 2013 effects
Фивел
Universal major 4
смешарики
cum
Pushpa 2 rashmika mandanna
Поиск - потеряний снайпер
masculine men
Fap teen
Finger family boo boo song
Новини