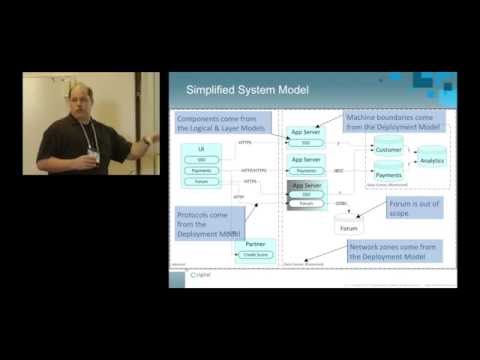
In my earlier video I explained the concept of Threat analysis and the STRIDE threat classification scheme. In that video I looked at the theory, but in this video I’m going to take a look at how it can be used in a real example using an Internet of Things (IoT) project. More details about the analysis are available on my website at: The example project used is my Raspberry Pi Pixel Server: This started life as a non-secure application designed for use on a secure network, but as I wanted to make it suitable for the IoT I decided I needed to implement the CIA triad and the AAA security framework. This also meant that I should perform cybersecurity threat analysis to ensure that the application is secure before connecting it to the Internet. This is also one of the key learning points in CISSP section 1. The 6 steps to STRIDE are: Spoofing Tampering Repudiation Information Disclosure Denial of Service DoS Elevation of privilege This video looks at creating data flow diagrams, the Microsoft Threat Analysis tool and the STRIDE analysis. One of the key things for the project is enabling https through an nginx reverse proxy. This is explained in this video: This video explains about how you can enable 2FA on an ssh server (such as a Raspberry Pi or other Linux computer): Why passwords are bad: Guide to hacking / cracking passwords: Chapters: 00:00 Introduction STRIDE 01:01 Microsoft Threat Modelling Tool 01:51 Raspberry Pi Pixel Server 03:22 Data flow diagram 05:43 Analysis http 08:09 Analysis https 12:25 Data flow diagram 2 12:49 Analysis file system 14:06 Software lifecycle 14:32 Threats to address 25:24 Summary
- 6335Просмотров
- 3 года назадОпубликованоPenguin Fortress - Cybersecurity Information
Cybersecurity STRIDE working example threat analysis
Похожее видео
Популярное
Bing shut down itv
лалапупси реклама
Tschu tschu wa
маша и мед
Preview 2 oh yeah
Universal dement
Alizeh agnihotri
baywatch
паляниця
ПОТЕРЯННЫЙ СНАЙПЕР 5 сери
6 серия
потеряный снайпер 3 серия
тупи и бину
Вулиця сезам
потерянный снайпер 2
Valu temporada
Грань правосудия 1 серия
2 сезон городской снайпер
Даша-следопыт - Даша ковбой
Wb 2002
masculine men
Красная гадюка 4
Стражи правосудия 5
Красная годюка
лалапупси реклама
Tschu tschu wa
маша и мед
Preview 2 oh yeah
Universal dement
Alizeh agnihotri
baywatch
паляниця
ПОТЕРЯННЫЙ СНАЙПЕР 5 сери
6 серия
потеряный снайпер 3 серия
тупи и бину
Вулиця сезам
потерянный снайпер 2
Valu temporada
Грань правосудия 1 серия
2 сезон городской снайпер
Даша-следопыт - Даша ковбой
Wb 2002
masculine men
Красная гадюка 4
Стражи правосудия 5
Красная годюка
Новини