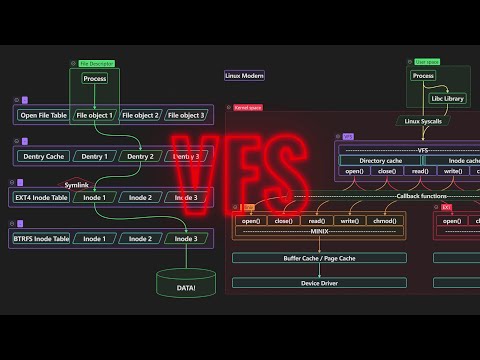
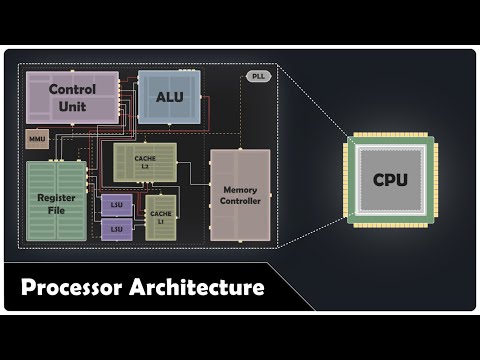
Interrupts in modern computers are a fascinating topic. They are absolutely essential in our modern high-performance systems. They serve both as a communication mechanism between peripheral device and the CPU, and as a way of interrupting a processor's execution to handle something important. SUMMARY Interrupts are signals that tell the processor that something important has happened and its immediate attention is required. These signals can be triggered by all sorts of events. For instance, moving your mouse, pressing a key on the keyboard, a storage device finishing a data transfer, or new data arriving in your network card's buffer can all generate an interrupt. Interrupts can be categorized into two main groups: • Hardware Interrupts: Asynchronous events typically generated by peripheral hardware devices. Can be delivered to a processor by either IRQ lines, which are dedicated physical lines, or by using Message-Signaled Interrupts (MSI), which uses the modern PCI Express bus to write interrupt messages directly into the processor's interrupt controller. • Software Interrupts (Exceptions): synchronous events generated by the processor when something unusual or important happens during the execution of an instruction. Exceptions don't need to be delivered to the CPU since they're generated by the CPU itself. They can be further divided into sub-types: Faults, Traps, and Aborts. Each hardware interrupt and exception is uniquely identified by its Interrupt Vector Number, which ranges from 0 to 255. Exceptions have constant numbers, typically from 0-31, while hardware interrupts are identified by vector numbers chosen by device drivers from the available range, usually 32-255. Handling an interrupt involves three steps: 1. Storing the state of the currently running process. 2. Calling the appropriate ISR, which then performs the necessary work to handle the interrupt. 3. Either restore the state of the running process or, in some cases, terminate it LINKS 📚 Computer Memory and Architecture E-Book Collection: 📚 Inside the Core: How the CPU Works (E-Book): 📚 Interrupts in Modern Computer Systems (E-Book): 📚 The Anatomy of Virtual Memory (E-Book): 📚 Beginner's Guide to CPU Caches (E-Book): ❤ Support my work: SOURCES The information in this video is based on my book: Interrupts in Modern Computer Systems. TABLE OF CONTENTS 00:00 Introduction 01:26 Defining Interrupts 02:43 Overview of Interrupt Handling 03:26 Hardware Interrupts 03:52 Interrupt Request (IRQ) Lines 04:58 Message-Signaled Interrupts (MSI) 05:30 Hardware Interrupt Detection 06:19 Software Interrupts (Exceptions) 07:30 Interrupt Vector Numbers 08:00 Servicing Interrupts 09:22 Interrupts in Modern Computer Systems (E-Book) ATTRIBUTION Some of the elements in the video were designed by vectorpocket / macrovector / / Freepik at . #computerscience #memorymanagement #computermemory #operatingsystem #interrupts
- 29799Просмотров
- 4 месяца назадОпубликованоBitLemon
How Interrupts Work in Modern Computers
Похожее видео
Популярное
Черная химера
оазис
Дельфин
ПОТЕРЯННЫЙ СНАЙПЕР2
Голие школьниц
Красная гадюка 12 серія
Красная гадюка 6 серия
Лупдиду
Волчий берег5серия
flip the frog the goal rush
Bing but it’s ruined in sora 2
Wb effects not scary
Потерянный спайпер 2
Красный тарантул 3
карусель
Потераний снайпер 2
союзмультфильм
комедия
undefined
C p
сорванцы
Городской снаипер 2
Крізь помилки минулого
потерений снайпер
forsaken fandom
оазис
Дельфин
ПОТЕРЯННЫЙ СНАЙПЕР2
Голие школьниц
Красная гадюка 12 серія
Красная гадюка 6 серия
Лупдиду
Волчий берег5серия
flip the frog the goal rush
Bing but it’s ruined in sora 2
Wb effects not scary
Потерянный спайпер 2
Красный тарантул 3
карусель
Потераний снайпер 2
союзмультфильм
комедия
undefined
C p
сорванцы
Городской снаипер 2
Крізь помилки минулого
потерений снайпер
forsaken fandom
Новини