=============================================== QUANTUM OBJECTS TO MULTIVERSE =============================================== [1] QUANTUM OBJECT ------------------ Definition: Fundamental particles or systems that exhibit quantum mechanical properties Key Properties: - Wave-particle duality (behaves as both wave and particle) - Quantum superposition (exists in multiple states simultaneously) - Quantum entanglement (instantaneous correlation with other particles) - Uncertainty principle (position and momentum cannot be precisely known) - Discrete energy levels Examples: Photons, electrons, quarks, atoms in quantum states [2] SUBATOMIC PARTICLES ----------------------- Definition: Particles smaller than atoms that constitute matter Categories: - Fermions (matter particles): quarks, leptons - Bosons (force carriers): photons, gluons, W/Z bosons, Higgs Properties: - Spin (intrinsic angular momentum) - Charge (electric, color, weak) - Mass (some massless like photons) - Governed by quantum field theory [3] ATOMS --------- Definition: Basic unit of matter consisting of nucleus and electrons Structure: - Nucleus: protons + neutrons - Electron cloud: probability distributions around nucleus - Energy levels: discrete electron orbital states - Size: ~10^-10 meters Quantum behavior: Electron transitions, atomic spectra, chemical bonding [4] MOLECULES ------------- Definition: Groups of atoms bonded together Formation: Chemical bonds (covalent, ionic, metallic) Properties: - Molecular orbitals (quantum mechanical description) - Vibrational and rotational energy states - Electronic transitions - Chemical reactivity Examples: H2O, DNA, proteins, polymers [5] QUANTUM FIELDS ------------------ Definition: Fundamental entities from which particles emerge as excitations Concept: Space filled with fields; particles are field vibrations Types: - Electromagnetic field → photons - Electron field → electrons/positrons - Quark fields → quarks - Higgs field → mass generation Governed by: Quantum field theory, Standard Model [6] QUANTUM SYSTEMS ------------------- Definition: Any system described by quantum mechanics Characteristics: - Wave function describes system state - Observable quantities have probability distributions - Measurement causes wave function collapse - Entanglement between subsystems possible Examples: Quantum dots, superconductors, quantum computers [7] MACROSCOPIC OBJECTS ----------------------- Definition: Large-scale objects where quantum effects usually average out Properties: - Classical behavior emerges from quantum foundations - Decoherence suppresses quantum interference - Thermal fluctuations dominate - Deterministic motion (classical mechanics) Examples: Everyday objects, planets, biological systems [8] ASTRONOMICAL OBJECTS ------------------------ Definition: Large-scale structures in space Categories: - Stars: fusion-powered plasma spheres - Planets: gravitationally rounded bodies orbiting stars - Galaxies: collections of billions of stars - Black holes: extreme gravitational objects - Nebulae: interstellar gas and dust clouds Scale: Light-years to billions of light-years [9] COSMIC STRUCTURES --------------------- Definition: Largest organized structures in the universe Hierarchy: - Galaxy clusters: groups of galaxies - Superclusters: clusters of galaxy clusters - Cosmic web: filaments and voids - Observable universe: ~93 billion light-years diameter Formation: Gravity acting on dark matter and ordinary matter [10] UNIVERSE ------------- Definition: All of space, time, matter, and energy that exists Properties: - Age: ~13.8 billion years - Expanding (accelerating expansion) - Contains: ~5% ordinary matter, ~27% dark matter, ~68% dark energy - Governed by general relativity on large scales - May be infinite in extent [11] MULTIVERSE --------------- Definition: Hypothetical collection of multiple universes Types (theoretical): - Level I: Infinite space beyond observable universe - Level II: Universes with different physical constants - Level III: Many-worlds quantum interpretation - Level IV: Mathematical universe hypothesis Status: Highly speculative, not directly observable Implications: Ultimate reality may be far larger than our universe =============================================== SCALE PROGRESSION: 10^-35m (Planck) → 10^26m (Observable Universe) COMPLEXITY EMERGENCE: Quantum → Classical → Cosmic → Multiverse =============================================== Game : Orders of Magnitude Steam : Music : From YouTube Audio Library Keywords : quantum physics, multiverse theory, planck length, quantum mechanics, string theory, parallel universes, quantum realm, cosmic scale, theoretical physics, quantum field theory From Quantum Object to The Multiverse - The 13 Minute Journey!
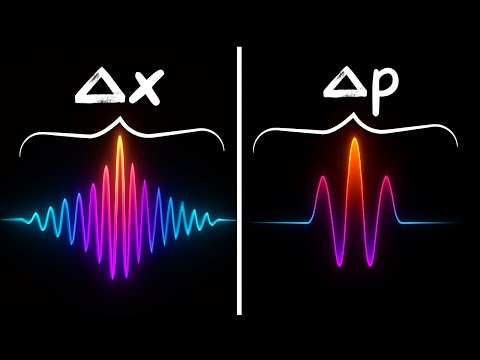
- 203026Просмотров
- 6 месяцев назадОпубликованоAnimagar
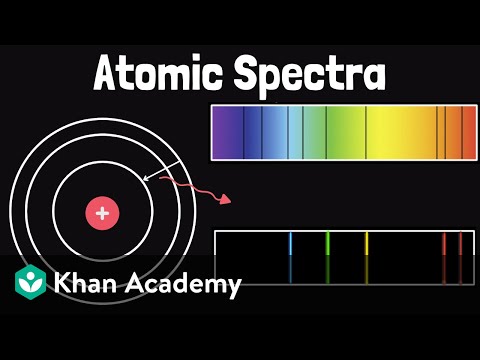
From Quantum Object to The Multiverse - The 13 Minute Journey!
Похожее видео
Популярное
Лихач 3 сезон 1-4
Стражи правосуддя 5
макароны спагетти рецепт
Рики Смешарики
щенячий патруль реклама
6 серия
Trade scam script
история графини де вержи
ВОЛШЕБНАЯ КАРУСЕЛЬ
Красуня гадюка3
Bing gets 3 strikes
РЫЦАРЬ МАЙК
Семья от а до Я
https:/www.google.com/url
przepraszamy za usterki
Божественний доктор
Потеринний снайпер 5
Потерянный снайпер 6серия
Городской снайпер 2 серия
Resila osta
Грань правосудия
terminal
смешарики
Indian idol season 15 jai jai shiv shankar
Стражи правосуддя 5
макароны спагетти рецепт
Рики Смешарики
щенячий патруль реклама
6 серия
Trade scam script
история графини де вержи
ВОЛШЕБНАЯ КАРУСЕЛЬ
Красуня гадюка3
Bing gets 3 strikes
РЫЦАРЬ МАЙК
Семья от а до Я
https:/www.google.com/url
przepraszamy za usterki
Божественний доктор
Потеринний снайпер 5
Потерянный снайпер 6серия
Городской снайпер 2 серия
Resila osta
Грань правосудия
terminal
смешарики
Indian idol season 15 jai jai shiv shankar
Новини