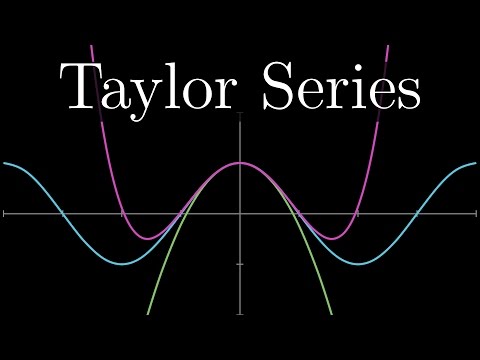
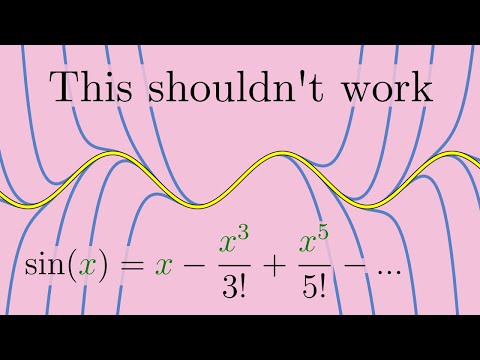
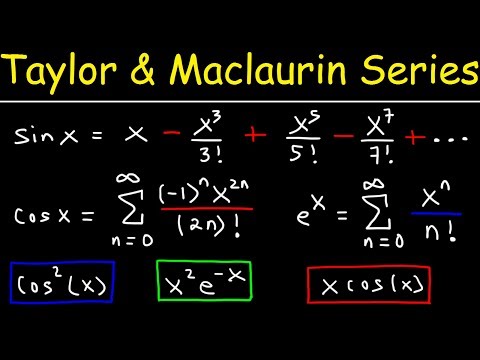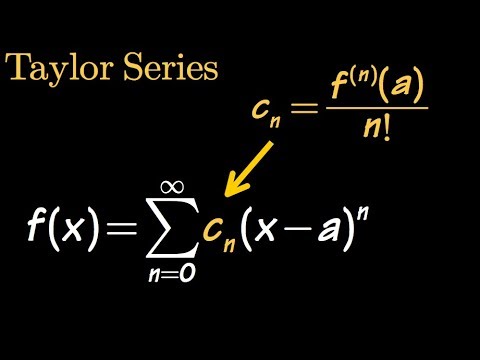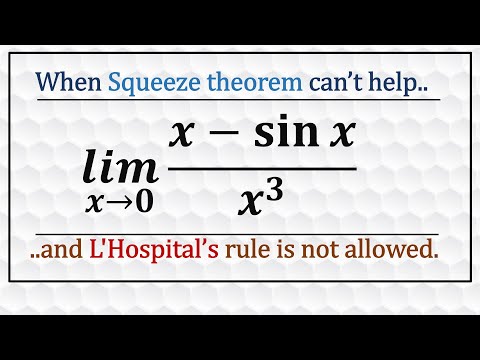University of Oxford mathematician Dr Tom Crawford derives Taylor's Theorem for approximating any function as a polynomial and explains how the expansion works with two detailed examples. Test yourself with some exercises on Taylor's Theorem with this FREE worksheet in Maple Learn: The video begins by introducing the idea of approximating a function by a polynomial and the condition we choose to implement that allows the coefficients to be derived. By ensuring that both the function and polynomial approximation are equal for all derivatives at a single point, Cauchy's Mean Value Theorem can be applied to give equality. Taylor's Theorem is demonstrated with two fully worked examples. First, the power series expansion for cos is derived by expanding around zero. Next, a third degree polynomial approximation is calculated for small x, when expanding the function ln(1+sin(x)). Check your working using the Maple Calculator App – available for free on Google Play and the App Store. Android: Apple: Other videos in the Oxford Calculus series can be found here: Finding critical points for functions of several variables: Classifying critical points using the method of the discriminant: Partial differentiation explained: Second order linear differential equations: Integrating factors explained: Solving simple PDEs: Jacobians explained: Separation of variables integration technique explained: Solving homogeneous first order differential equations: Find out more about the Maple Calculator App and Maple Learn on the Maplesoft YouTube channel: Produced by Dr Tom Crawford at the University of Oxford. Tom is an Early-Career Teaching and Outreach Fellow at St Edmund Hall: For more maths content check out Tom's website You can also follow Tom on Facebook, Twitter and Instagram @tomrocksmaths. Get your Tom Rocks Maths merchandise here:
- 182923Просмотров
- 3 года назадОпубликованоTom Rocks Maths
Oxford Calculus: Taylors Theorem Explained with Examples and Derivation
Похожее видео
Популярное
war thunder tech tree
Badalados assistimos 2022
потеряный снайпер 3 серия
Sprunki oc real v3 part 3/3
малыш вилли 03
mickey Valentine day party part 2
хулиган и пай девочка
Cartoon network russian
Indian idol season 15 jai jai shiv shankar
Бурное,безрассуудствоо
Потерянный снайпер сериал
МОЛАНГ
Alizeh agnihotri
веселая-карусел-25
ЗАБОТЛИВЫЕ МИШКИ
ЛЕТО НА ТИЖИ
Beast rogue lion
НЕПОСЕДА ЗУ
бен 10 реклама
Tantric awakening shaft
Поточний снайпер 2 часть
oggy
Universal pictures 1997 2012 1997
психушка
губка боб хорошие соседи
Badalados assistimos 2022
потеряный снайпер 3 серия
Sprunki oc real v3 part 3/3
малыш вилли 03
mickey Valentine day party part 2
хулиган и пай девочка
Cartoon network russian
Indian idol season 15 jai jai shiv shankar
Бурное,безрассуудствоо
Потерянный снайпер сериал
МОЛАНГ
Alizeh agnihotri
веселая-карусел-25
ЗАБОТЛИВЫЕ МИШКИ
ЛЕТО НА ТИЖИ
Beast rogue lion
НЕПОСЕДА ЗУ
бен 10 реклама
Tantric awakening shaft
Поточний снайпер 2 часть
oggy
Universal pictures 1997 2012 1997
психушка
губка боб хорошие соседи
Новини