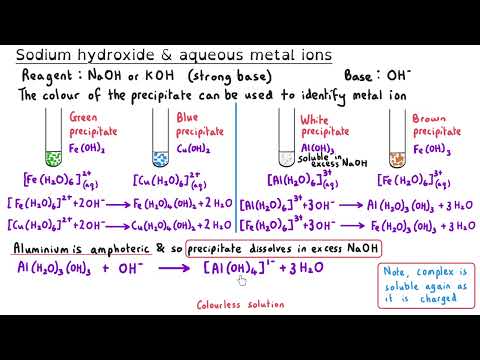
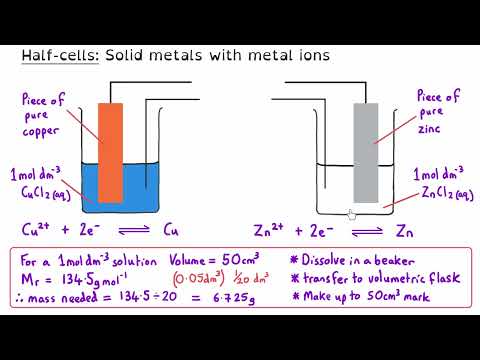
Transition Metals | Ultimate Guide | Full Topic | A Level Chemistry Transition metals are some of the most versatile elements in the periodic table, forming complex ions, exhibiting variable oxidation states, and acting as catalysts in key industrial processes. In this A Level Chemistry masterclass, we break down everything you need to know about transition metals in one comprehensive video. Whether you're revising for exams or looking to deepen your understanding, this video is designed for all exam boards. 🔹 What You'll Learn: ✔️ Electron configurations & properties of transition metals ✔️ Complex ions, ligands, and isomerism ✔️ Why transition metals are coloured & how to use a colorimeter ✔️ Redox reactions, electrode potentials & redox titrations ✔️ Catalysis – homogeneous, heterogeneous & autocatalysis 📌 Timestamps 00:05 Introduction 00:20 What are transition metals? 01:24 Electron configuration of transition metals 05:22 General properties of transition metals 06:34 Complexes 09:19 Monodentate ligands 10:29 Shapes of complex ions 12:04 Bidentate ligands 14:55 Multidentate ligands 16:46 Drawing the shape and working out oxidation states 18:23 Tollens reagent 20:16 Geometric Isomerism | Cis-/trans- 21:39 Cisplatin 22:57 Optical Isomerism in complexes 25:12 Ligand substitution reactions 26:33 Substitution involving the chloride ligand 28:17 The chelate effect 31:41 Haem 33:46 How cisplatin works 35:43 Absorbing, transmitting, and reflecting light 37:10 Energy difference and the d sub-shell 40:37 Why are colours different? 43:23 Using a colorimeter 45:50 Calibration curves | Determining an unknown concentration 47:53 Variable oxidation states and electrode potentials 49:59 Redox potentials 52:03 Vanadium and Zinc 54:52 Redox titrations | Iron & Potassium Manganate (VII) 58:23 Redox titrations | Ethanedioate & Potassium Manganate (VII) 1:02:03 Redox titrations | Hydrogen Peroxide & Potassium Manganate (VII) 1:05:13 What are catalysts and how do they work? 1:06:53 Heterogeneous catalysts 1:08:15 How heterogeneous catalysts work 1:09:38 Catalyst efficiency and poisoning 1:11:23 The Contact Process and vanadium (V) oxide 1:13:33 Homogeneous catalysts 1:15:45 Iron (II) catalyst | Iodide ions and peroxodisulfate ions 1:18:51 Redox potentials and catalysis 1:20:47 Autocatalysis | Potassium manganate (VII) and ethanedioic acid 1:24:56 Investigating autocatalysis This A Level Chemistry masterclass gives you exam-ready explanations and real-world applications, perfect for AQA, OCR, Edexcel, and all exam boards! 🔗 Explore More: 🔹Inorganic Chemistry Year 1 Explanation videos Playlist: 🔹 Inorganic Chemistry Year 2 Explanation videos Playlist: 🔹 Inorganic Chemistry Exam Question Walkthrough Playlist: 🔹Inorganic Chemistry Multiple Choice Walkthrough Playlist: 📢 Connect with Us: 📷 Instagram: @chemistrytutor123 🎵 TikTok: @chemistrytutor123 📩 Email: thechemistrytutor123@ 📌 Hashtags: #alevelchemistry #transitionmetals #chemistryrevision #redoxreactions #complexions #catalysts #Colorimetry #chemistryexplained #exampreparation #chemistrymasterclass Correction: 02:15 I read the Ar for scandium instead of titanium. Titanium’s atomic number is 22. 04:53 The electron configurations for Sc³⁺ and Zn²⁺ should be [Ar] 3s².
- 45629Просмотров
- 8 месяцев назадОпубликованоThe Chemistry Tutor
Transition Metals | Ultimate Guide | Full Topic | A Level Chemistry
Похожее видео
Популярное
сильвания фэмили реклама
Бурное безрассудство 1
Красная гадюка часть ,6
Стражи правосуддя 5
Pushpa 2 rashmika mandanna
ПЕРСИ И ДРУЗЬЯ
сакс игрушки
шопкинс реклама
охотница
Сутінки розділ 3
cum
эвер афтер хай реклама
массаж поджелудочной
Стражи правосудия 3 сезон
Деревяшки
klaskyklaskyklasskyklasky joey 2 do go
Ох и ах
красная гадюка12серия
Фильм потеряны снайпер
потеряный снайпер 2 часть
Стражи правосудтя
Пим и Пэм 02c
ПОТЕРЯННЫЙ СНАЙПЕР 5 сери
Бурное безрассудство 1
Красная гадюка часть ,6
Стражи правосуддя 5
Pushpa 2 rashmika mandanna
ПЕРСИ И ДРУЗЬЯ
сакс игрушки
шопкинс реклама
охотница
Сутінки розділ 3
cum
эвер афтер хай реклама
массаж поджелудочной
Стражи правосудия 3 сезон
Деревяшки
klaskyklaskyklasskyklasky joey 2 do go
Ох и ах
красная гадюка12серия
Фильм потеряны снайпер
потеряный снайпер 2 часть
Стражи правосудтя
Пим и Пэм 02c
ПОТЕРЯННЫЙ СНАЙПЕР 5 сери
Новини